Have you ever encountered the frustrating “Error 404: The requested URL was not found on this server” message while browsing the web? This common issue can be a headache for both website owners and visitors alike. Not only does it disrupt the user experience, but it can also negatively impact your site’s search engine rankings and overall performance.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to fix 404 errors and get your website back on track. You’ll learn about the causes of these pesky “404 page not found” errors and discover five easy steps to resolve them. From updating permalinks to creating custom error pages, we’ll cover everything you need to know to improve your site’s functionality and keep your visitors happy. So, let’s dive in and tackle this problem head-on!
Understanding Error 404: Causes and Impact
What is Error 404?
Error 404, also known as “the requested URL was not found on this server,” is a standard HTTP status code that occurs when a user tries to access a webpage that doesn’t exist on the server. This error message indicates that while the server successfully received the request, it couldn’t find the specific page the user was looking for. It’s one of the most common errors encountered on the internet and has become a cultural reference for anything that’s missing or inaccessible.

Common causes of 404 errors
There are several reasons why you might encounter a 404 error:
- Deleted or moved content: The most frequent cause is when a website removes or relocates a page without updating internal links or setting up proper redirects.
- Incorrect URL: This can happen if a user types the wrong address, a developer makes a mistake during website creation, or there’s an improper link on the site.
- Server issues: Sometimes, a misconfigured server or a broken connection can lead to 404 errors.
- Domain changes: If a domain name no longer exists or can’t be converted to an IP address by the Domain Name System (DNS), it may result in a 404 error.
- Access restrictions: In some cases, a 404 error might appear when a user tries to access content they’re not authorized to view.
How 404 errors affect SEO and user experience
404 errors can have a significant impact on both search engine optimization (SEO) and user experience:
- User frustration: When visitors encounter a “404 page not found” error, it can be confusing and frustrating, especially if they were expecting to find important information.
- Increased bounce rates: Users are likely to leave your site quickly if they can’t find what they’re looking for, leading to higher bounce rates.
- Reduced crawl efficiency: Search engine crawlers may waste time on non-existent pages, potentially affecting the indexing of your site’s content.
- Loss of link equity: If a page with incoming links returns a 404 error, you lose the SEO value those links were passing to your site.
- Negative impact on rankings: While Google doesn’t directly penalize sites for 404 errors, a high number of broken links can signal poor site maintenance, potentially affecting your search rankings.
- Decreased site credibility: Frequent 404 errors can make your site appear unreliable or outdated, damaging your online reputation.
To mitigate these issues, it’s crucial to regularly check for and address 404 errors using tools like Google Search Console or Google Analytics. Creating custom 404 pages with helpful information and links can also improve user experience when errors do occur. By properly managing 404 errors, you can maintain a healthy website that both users and search engines trust.
Step 1: Check and Update Your Site’s Permalinks
To fix the “Error 404: The requested URL was not found on this server” issue, one of the first steps you should take is to check and update your site’s permalinks. This process can help resolve many 404 errors and improve your website’s overall functionality. Let’s go through the steps to access and update your permalinks settings.
Accessing WordPress dashboard
To begin, you need to log in to your WordPress admin dashboard. Open your web browser and enter your website’s URL followed by “/wp-admin” (e.g., www.yourwebsite.com/wp-admin). Enter your username and password to access the dashboard.
Navigating to permalink settings
Once you’re in the dashboard, follow these steps to find the permalink settings:
- Look for the “Settings” option in the left-side menu of your WordPress dashboard.
- Click on “Settings” to expand the submenu.
- Select “Permalinks” from the submenu options.
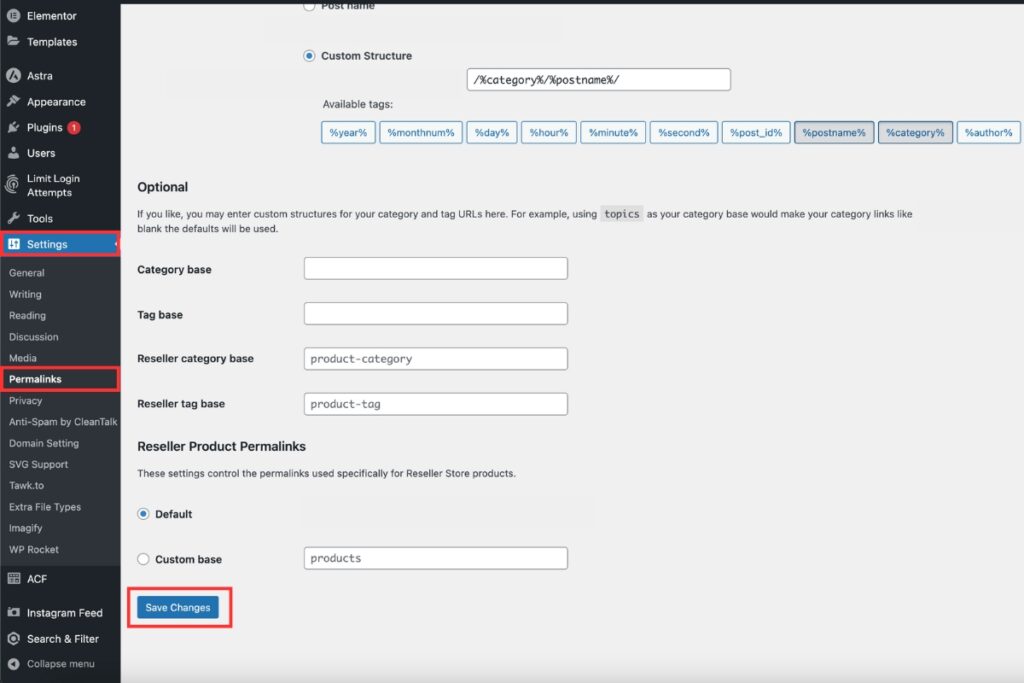
This will take you to the Permalink Settings screen, where you can view and modify your current permalink structure.
Saving changes without modifications
Even if you don’t want to make any changes to your current permalink structure, it’s a good idea to save the settings again. This action can help refresh your site’s permalink structure and resolve some 404 errors. Here’s what you need to do:
- On the Permalink Settings screen, scroll down to the bottom of the page.
- Without making any changes, click the “Save Changes” button.
This simple action triggers WordPress to flush its rewrite rules, which can often fix URL-related issues. After clicking “Save Changes,” you should see a confirmation message at the top of the screen saying “Permalink structure updated.”
If you encounter any issues while saving the changes, it might be due to your .htaccess file not being writable. In this case, WordPress will display a message with instructions on how to manually update your .htaccess file.
Remember, changing your permalink structure can have a significant impact on your site’s SEO and existing links. If you decide to modify the structure, make sure to set up proper redirects from old URLs to new ones to avoid creating more 404 errors.
By following these steps, you’ve taken an important first step in addressing the “Error 404: The requested URL was not found on this server” issue. This process helps ensure that your site’s permalink structure is correctly configured and can potentially resolve many 404 errors caused by URL-related problems.
Step 2: Set Up 301 Redirects for Moved Content
Setting up 301 redirects is a crucial step in fixing the “Error 404: The requested URL was not found on this server” issue. These redirects tell search engines and browsers that a page has been permanently moved to a new location, ensuring users are directed to the correct content and search engines can update their indexes accordingly.
Identifying moved or renamed pages
To begin, you need to identify the pages that have been moved or renamed on your website. This process involves:
- Reviewing your site structure changes
- Checking Google Search Console for crawl errors
- Analyzing Google Analytics data to spot 404 errors
By examining this information, you can create a list of URLs that need redirection, helping you maintain your site’s SEO value and provide a seamless user experience.
Using plugins for redirect management
For WordPress users, several plugins can simplify the process of managing redirects. Some popular options include:
- Redirection: This free plugin allows you to easily create and manage 301 redirects without needing Apache or Nginx knowledge. It can also automatically create redirects when post or page permalinks change.
- 301 Redirects: A free plugin that enables you to set up 301, 302, and 307 redirects. It also provides a 404 error log to help you track and fix errors.
- All in One SEO: While primarily an SEO plugin, its premium version includes a powerful redirection manager that supports various status codes.
These plugins offer user-friendly interfaces to add redirects, monitor 404 errors, and improve your site’s overall health.
Implementing server-level redirects
For more advanced users or those not using WordPress, implementing server-level redirects is an option. This method involves editing your server configuration files:
- Apache servers: Edit the .htaccess file to add redirect rules. For example:
Redirect 301 /old-page.html https://www.yourwebsite.com/new-page.html - Nginx servers: Modify the server block in your Nginx configuration file:
location /old-page.html { return 301 https://www.yourwebsite.com/new-page.html; }
Remember to back up your configuration files before making changes and test your redirects thoroughly to ensure they’re working correctly.
By setting up 301 redirects, you’re not only fixing the “Error 404: The requested URL was not found on this server” issue but also improving your site’s SEO. These redirects help preserve link equity, maintain user experience, and ensure that search engines can find and index your content correctly. Whether you choose to use plugins or implement server-level redirects, this step is essential in managing your site’s structure and preventing 404 errors.
Step 3: Create a Custom 404 Error Page
Creating a custom 404 error page is an essential step in addressing the “Error 404: The requested URL was not found on this server” issue. A well-designed 404 page can transform a potentially frustrating experience into an opportunity to engage users and guide them back to your site’s content.
Designing an informative and user-friendly 404 page
When designing your custom 404 page, focus on clarity and helpfulness. Start with a clear, concise message explaining that the requested URL was not found on this server. Use simple language that your target audience can easily understand, avoiding technical jargon unless your visitors are tech-savvy.
To make your 404 page more engaging:
• Add a touch of humor or creativity to lighten the mood • Include your brand’s logo and maintain consistent design elements • Keep the content brief and easy to scan • Use visually appealing graphics or illustrations that align with your website’s style
Including search functionality and navigation options
To help users find what they’re looking for, add these features to your 404 page:
• Search bar: This allows visitors to search for the content they were initially seeking • Navigation menu: Include links to your most important pages, such as the homepage, popular articles, or product categories • Suggested content: Offer links to your most visited pages or recent blog posts
By providing these options, you give users multiple ways to continue their journey on your website, reducing the likelihood of them leaving due to frustration.
Optimizing 404 page for performance
To ensure your custom 404 page serves its purpose effectively:
• Keep it lightweight: Minimize file sizes and avoid heavy scripts or large images to ensure fast loading times • Make it responsive: Ensure your 404 page looks good and functions well on all devices, from desktop computers to smartphones • Test thoroughly: Check that all links, search functionality, and navigation options work correctly
Remember, the goal of your 404 page is to keep users engaged and guide them back to functioning parts of your website. By implementing these strategies, you can turn a potential dead-end into a useful tool for improving user experience and reducing bounce rates.
To further enhance your 404 page’s effectiveness, consider using Google Search Console and Google Analytics to track 404 errors and user behavior. This data can help you identify common causes of 404 errors and refine your page accordingly.
By creating a custom 404 error page that is informative, user-friendly, and optimized for performance, you’re taking a significant step in addressing the “Error 404: The requested URL was not found on this server” issue. This approach not only improves user experience but also contributes to better SEO performance by keeping visitors engaged with your site.
Conclusion
Tackling the “Error 404: The requested URL was not found on this server” issue is crucial to enhance your website’s performance and user experience. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively address this common problem and keep your visitors engaged. From updating permalinks to creating custom error pages, these strategies help maintain your site’s SEO value and provide a smoother browsing experience for your audience.
Remember, fixing 404 errors is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and maintenance. By staying on top of these issues, you’re not just solving a technical problem – you’re showing your visitors that you care about their experience on your site. This attention to detail can boost your site’s credibility, improve user satisfaction, and ultimately contribute to the success of your online presence.
FAQs
1. How can I resolve the ‘Error 404: The Requested URL Was Not Found on This Server’?
To address ‘Error 404: The Requested URL Was Not Found on This Server’, you can try several methods:
- Refresh the page to ensure it wasn’t a one-time error.
- Clear your browser’s cache which might be holding onto outdated information.
- Update the permalinks on your site if you’re using a content management system like WordPress.
- Implement 301 redirects for any content that has been moved or renamed.
- Temporarily disable the ‘.htaccess’ file to check if it’s causing the issue.
2. What are some tips for fixing a 404 server error?
If you encounter a 404 server error, consider the following strategies:
- Refresh the webpage as it might not have loaded correctly.
- Verify the URL for any errors as a small typo could lead to a 404 error.
- Use a search engine to find the correct page.
- Access the webpage from a different device to rule out device-specific issues.
- Clear your browser cache and delete cookies which may solve the problem.
- Set up a custom 404 error page that helps users when they land on a non-existing page.
- Create redirects for pages that have been moved to maintain a good user experience.
- Make sure all internal links pointing to the page are correct.
3. How can I remove a URL that shows a 404 error from Google’s search results?
To remove a URL that displays a 404 error from Google’s search results, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the ‘HTTP errors’ section in Google Search Console.
- Select the URLs you want to remove from the list showing a 404 error.
- Click on ‘Request Removal’ at the top of the page.
- You will be prompted to provide a reason for the removal request.
4. What should I do if I encounter HTTP Error 404 ‘The requested resource is not found’?
If you come across HTTP Error 404, you can:
- Double-check the URL for any typing mistakes as even a minor error can cause this issue.
- Refresh the webpage since the error might be temporary.
- Search the web for the correct page.
- Try accessing the page from a different device to see if the issue persists.
- Use the Internet Archive’s Wayback Machine to find a cached version of the page.
- Contact the website’s administrator for further assistance if the problem continues.
